What are the best health insurance plans for seniors? This question is on the minds of many as they navigate the complex world of healthcare coverage. As we age, our health needs evolve, and finding the right insurance plan becomes crucial.
This guide will explore the different options available to seniors, helping you make informed decisions about your coverage.
We’ll delve into the intricacies of Medicare, its various parts, and the advantages and disadvantages of each. We’ll also discuss other senior-specific health insurance plans, including Medicare Advantage and Medigap, outlining their coverage, costs, and eligibility requirements.
Understanding Senior Health Insurance Needs
As you age, your health insurance needs change. Seniors face unique health challenges that require specialized coverage. Understanding these needs is crucial for choosing the right health insurance plan.
Health Needs of Seniors
Seniors are more likely to experience chronic health conditions like heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and cancer. These conditions often require ongoing medical care, prescription drugs, and specialized treatments. Additionally, seniors may have difficulty managing multiple medications and navigating the healthcare system.
Common Health Concerns Faced by Seniors
- Chronic Diseases:As mentioned earlier, seniors are more susceptible to chronic diseases that require long-term management. These conditions can lead to frequent doctor visits, hospital stays, and expensive medications.
- Mental Health Issues:Seniors may experience increased risk of depression, anxiety, and dementia. These conditions can impact their overall well-being and require specialized care.
- Falls and Injuries:Seniors are more prone to falls and other injuries, which can lead to hospitalizations, rehabilitation, and long-term care needs.
- Vision and Hearing Loss:Age-related vision and hearing loss can significantly impact daily life and require specialized medical attention.
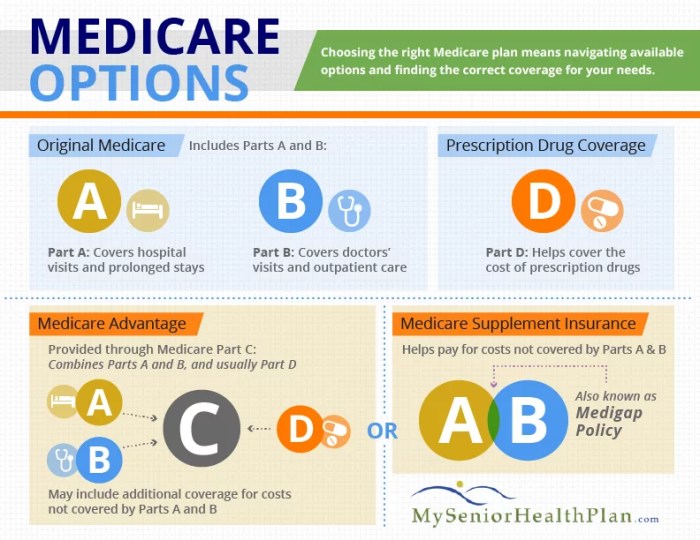
Medicare: A Comprehensive Overview
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people aged 65 and older, as well as individuals with certain disabilities. It’s a complex program with different parts, each covering specific healthcare needs.
Understanding Medicare Parts
Medicare is divided into four main parts:
- Part A (Hospital Insurance):Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health services.
- Part B (Medical Insurance):Covers doctor visits, outpatient care, preventive services, and some durable medical equipment.
- Part C (Medicare Advantage):Offered by private insurance companies, it combines Part A, Part B, and sometimes Part D coverage into a single plan. It may offer additional benefits like vision, dental, and hearing coverage.
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage):Covers prescription drugs, but requires enrollment in a separate plan. It’s offered by private insurance companies.
Benefits and Limitations of Medicare
Medicare provides essential health insurance coverage for seniors, but it has limitations:
- Coverage Gaps:Medicare doesn’t cover all medical expenses. There are deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance that seniors must pay out-of-pocket.
- Limited Coverage for Long-Term Care:Medicare doesn’t cover long-term care, such as assisted living or nursing home care. This can be a significant financial burden for seniors and their families.
- Out-of-Pocket Costs:Medicare beneficiaries may face substantial out-of-pocket costs, particularly for prescription drugs and specialized treatments.
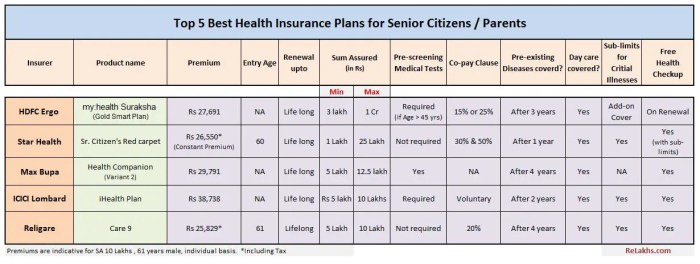
Types of Senior Health Insurance Plans
Navigating the world of senior health insurance can feel like entering a maze, but understanding the different plan types can help you find the right path for your needs. Each plan offers unique coverage, costs, and eligibility criteria, so let’s break down the key options available.
Medicare Advantage
Medicare Advantage plans, also known as Medicare Part C, are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans combine Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance) into a single plan. Medicare Advantage plans provide a variety of benefits, including:
- Coverage for prescription drugs: Many plans include prescription drug coverage, which can be a significant advantage for seniors who need regular medications.
- Vision, dental, and hearing benefits: Some plans offer additional benefits like vision, dental, and hearing coverage, which can be valuable for maintaining overall health.
- Lower monthly premiums: Compared to traditional Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans may have lower monthly premiums, which can be attractive for seniors on a fixed income.
- Health and wellness programs: Many plans offer health and wellness programs, such as disease management programs, that can help seniors stay healthy and manage chronic conditions.
However, Medicare Advantage plans also have some potential drawbacks:
- Limited network of providers: You may need to see providers within a specific network, which can limit your choice of doctors and hospitals.
- Potential for higher out-of-pocket costs: While monthly premiums may be lower, out-of-pocket costs, such as copays and deductibles, can be higher than traditional Medicare.
- Limited access to specialists: You may need to get referrals to see specialists, which can create delays in receiving care.
To be eligible for Medicare Advantage, you must be enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B. You can enroll during the annual open enrollment period or during a special enrollment period if you meet certain criteria.
Medigap
Medigap plans, also known as Medicare Supplement Insurance, are supplemental health insurance policies that help cover some of the out-of-pocket costs associated with Original Medicare (Parts A and B).Medigap plans offer the following benefits:
- Reduced out-of-pocket costs: Medigap plans can significantly reduce your out-of-pocket costs for things like deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments.
- Access to any Medicare-approved provider: Medigap plans allow you to see any Medicare-approved provider in the country, providing greater flexibility in choosing your healthcare providers.
- Predictable costs: Medigap plans have standardized benefits, making it easier to predict your out-of-pocket costs.
However, Medigap plans also have some disadvantages:
- Higher monthly premiums: Medigap plans generally have higher monthly premiums than Medicare Advantage plans.
- Limited coverage for prescription drugs: Medigap plans do not cover prescription drugs, so you’ll need to purchase a separate prescription drug plan (Medicare Part D).
- Not available in all states: Medigap plans are not available in all states, and the availability and costs may vary depending on your location.
To be eligible for Medigap, you must be enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B. You can purchase a Medigap plan during a specific enrollment period after turning 65 or during a special enrollment period if you meet certain criteria.
Medicare Part D
Medicare Part D is a prescription drug coverage program that helps seniors pay for their medications. It is a voluntary program, and you can choose from a variety of plans offered by private insurance companies.Medicare Part D plans offer the following benefits:
- Coverage for prescription drugs: Part D plans provide coverage for a wide range of prescription drugs, helping seniors manage the costs of their medications.
- Variety of plan options: You can choose from a variety of plans based on your individual needs and budget.
- Lower out-of-pocket costs: Part D plans can help reduce your out-of-pocket costs for prescription drugs.
However, Medicare Part D plans also have some disadvantages:
- Coverage gaps: Part D plans have coverage gaps, known as the “donut hole,” where you are responsible for a higher percentage of the cost of your medications. However, the Affordable Care Act has significantly reduced the size of the donut hole.
- Monthly premiums: You will need to pay a monthly premium for your Part D plan.
- Formulary restrictions: Part D plans have formularies, which are lists of covered medications. You may need to switch medications to one that is covered by your plan.
To be eligible for Medicare Part D, you must be enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B. You can enroll in a Part D plan during the annual open enrollment period or during a special enrollment period if you meet certain criteria.
Other Senior Health Insurance Options
In addition to the plans discussed above, there are other health insurance options available for seniors, including:
- Employer-sponsored health insurance: If you are still working, you may be eligible for health insurance through your employer.
- State health insurance programs: Some states offer health insurance programs for low-income seniors.
- Long-term care insurance: Long-term care insurance can help cover the costs of long-term care services, such as nursing home care or assisted living.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Plan

Choosing the right health insurance plan for your senior years is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your financial well-being and overall health. While we’ve already explored the different types of senior health insurance plans, it’s equally important to consider your individual needs and preferences when making your final selection.
Understanding Individual Needs and Preferences, What are the best health insurance plans for seniors?
Senior health insurance plans are designed to cater to the unique needs of older adults. However, each individual has specific health concerns, lifestyle choices, and financial limitations that should be taken into account. For instance, someone with chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease will prioritize plans with comprehensive coverage for their specific needs.
Conversely, someone who is relatively healthy and active might opt for a plan with lower premiums but fewer benefits.
Enrollment and Cost Considerations
Navigating the enrollment process and understanding the cost implications of senior health insurance plans is crucial for making informed decisions. This section delves into the enrollment procedures for Medicare and other senior health insurance plans, explores the various cost components, and provides resources for finding financial assistance options.
Finding the right health insurance plan for seniors can be a real maze, with Medicare, Medigap, and Advantage plans all vying for your attention. But what if you’re also thinking about life insurance? If you’re considering a policy that can convert to permanent coverage, then you might want to check out what are convertible life insurance policies?
. These policies can offer flexibility and peace of mind, especially if your health needs change down the road. So, when choosing your senior health insurance, remember to factor in the possibility of life insurance, too!
Medicare Enrollment
Medicare enrollment is a phased process, with different eligibility periods and options depending on your specific circumstances.
- Initial Enrollment Period (IEP):This period begins three months before your 65th birthday, includes your birthday month, and ends three months after your birthday. During this time, you can enroll in Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) without penalty.
- Special Enrollment Period (SEP):If you miss your IEP, you may qualify for a SEP if you meet specific criteria, such as losing employer-sponsored health insurance or moving to a new area.
- General Enrollment Period (GEP):This period runs from January 1st to March 31st each year. However, if you enroll during the GEP, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty.
Other Senior Health Insurance Plans
Besides Medicare, you may also consider enrolling in other senior health insurance plans to supplement your coverage.
- Medicare Advantage (Part C):These plans are offered by private insurance companies and provide comprehensive coverage, often including prescription drugs, vision, and dental. You can enroll during your IEP, SEP, or during the annual Open Enrollment Period (October 15th to December 7th).
- Medicare Supplement Insurance (Medigap):These plans are also offered by private insurance companies and help pay for out-of-pocket costs associated with Original Medicare. You can enroll during your IEP or during a six-month period following your 65th birthday.
- Prescription Drug Coverage (Part D):This coverage is offered through private insurance companies and helps pay for prescription drugs. You can enroll during your IEP, SEP, or during the annual Open Enrollment Period (October 15th to December 7th).
Cost Considerations
The cost of senior health insurance plans varies depending on the plan type, coverage level, and individual factors.
- Premiums:These are monthly payments you make for your health insurance coverage.
- Deductibles:These are fixed amounts you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins.
- Copayments:These are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor visits or prescription drugs.
- Coinsurance:This is a percentage of the cost of covered services that you pay.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum:This is the maximum amount you will have to pay out-of-pocket for covered services in a given year.
Financial Assistance Options
If you are struggling to afford your senior health insurance premiums, you may be eligible for financial assistance.
- Medicare Savings Programs (MSPs):These programs help low-income individuals pay for Medicare premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance.
- Extra Help with Medicare Prescription Drug Costs:This program helps low-income individuals pay for prescription drug costs.
- State Health Insurance Assistance Programs (SHIPs):These programs provide free counseling and assistance to seniors navigating the Medicare system and finding affordable health insurance options.
Staying Informed and Making Adjustments: What Are The Best Health Insurance Plans For Seniors?
Your health insurance needs can change over time, so it’s essential to stay informed and make adjustments as necessary. Reviewing your plan annually ensures it continues to meet your evolving needs and protects you from potential gaps in coverage.
Annual Plan Review
It’s crucial to review your health insurance plan at least once a year, ideally during the annual open enrollment period. This period typically runs from October 15th to December 7th each year. During this time, you can make changes to your plan without needing a special reason.
- Check for changes in your coverage:Insurance companies can adjust their plans, including benefits, premiums, and deductibles. A review helps you understand any modifications and ensure your plan remains suitable.
- Evaluate your healthcare needs:As you age, your health needs may change. You might require more frequent doctor visits, prescription medications, or specialized care. This review allows you to adjust your coverage to reflect these changes.
- Compare plan options:The insurance market is constantly evolving, and new plans with different benefits and costs might become available. Comparing plans can help you find a more cost-effective option that better suits your current needs.
Making Changes to Your Plan
You can make changes to your health insurance plan throughout the year, but these changes may require a qualifying event, such as:
- Loss of job:If you lose your job, you may be eligible for a special enrollment period to change your plan.
- Moving to a new area:If you move to a new state or county, you may need to change your plan to one offered in your new location.
- Significant life changes:Life events like marriage, divorce, or the birth of a child can trigger a special enrollment period.
- Changes in your health:If your health significantly deteriorates, you may be eligible to change your plan to one with more comprehensive coverage.
Resources for Information and Support
Several resources can help you stay informed about senior health insurance:
- Medicare.gov:This official website provides comprehensive information about Medicare plans, eligibility, and enrollment. It also offers tools to compare plans and find local resources.
- State health insurance assistance programs:Most states offer programs that provide free counseling and assistance with choosing a health insurance plan. You can find contact information for your state’s program on the Medicare.gov website.
- Independent insurance agents:These agents can help you compare different plans and find one that meets your specific needs. They are typically compensated by the insurance companies, so their services are free to you.
End of Discussion
Choosing the right health insurance plan as a senior is a significant decision, one that should be approached with careful consideration and a clear understanding of your needs. By understanding the different plan options, their costs, and the factors to consider, you can confidently navigate the healthcare landscape and find the best coverage to meet your unique requirements.
Remember, staying informed and making necessary adjustments to your plan as your health needs evolve is key to ensuring you have the right coverage for a healthy and secure future.
Detailed FAQs
What is Medicare, and how does it work?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It’s divided into four parts: Part A (hospital insurance), Part B (medical insurance), Part C (Medicare Advantage), and Part D (prescription drug coverage).
How can I find financial assistance for my health insurance premiums?
You can explore options like the Medicare Savings Programs (MSPs) and Extra Help, which offer financial assistance to low-income individuals. The Social Security Administration and your state’s health insurance marketplace can provide more information.
Can I change my Medicare plan after I enroll?
Yes, you can make changes to your Medicare plan during the Annual Enrollment Period (AEP), which runs from October 15th to December 7th each year. You can also make changes outside of AEP if you qualify for a Special Enrollment Period (SEP) due to certain life events, such as moving or losing your job.