Fire insurance policy – a phrase that conjures images of charred remains and financial devastation. But it’s also a lifeline, a shield against the unexpected inferno that can consume not only your property but your peace of mind. Think of it as a safety net, catching you when disaster strikes.
This guide will delve into the world of fire insurance, exploring its intricacies, benefits, and the crucial role it plays in protecting what matters most.
Imagine a raging fire engulfing your home, leaving you with nothing but ashes and the weight of rebuilding. Fire insurance is the invisible hero, stepping in to cover the costs of repairs, replacements, and even lost income. But navigating the complex world of insurance policies can be a daunting task.
Fear not, for we’ll equip you with the knowledge to choose the right policy, understand its components, and navigate the claims process with confidence.
What is Fire Insurance?: Fire Insurance Policy
Fire insurance is a type of property insurance that protects you against financial losses caused by fire damage to your property. It provides coverage for repairs or replacement of your property, as well as any belongings that were destroyed or damaged in the fire.Fire insurance is crucial because fire incidents can lead to significant financial burdens.
The cost of rebuilding or repairing a damaged property, replacing lost belongings, and covering other related expenses can be overwhelming without adequate insurance coverage.
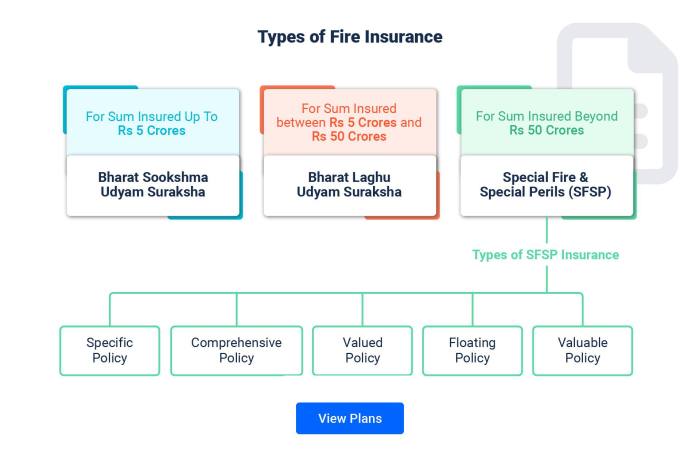
Types of Fire Insurance Policies
Different types of fire insurance policies are available, each offering varying levels of coverage and benefits.
Fire insurance policies are like trusty fire extinguishers for your home, providing a safety net in case of disaster. But just as you might want a long-term financial plan beyond just fire protection, you might consider Whole life insurance for a more comprehensive approach to your financial future.
While fire insurance shields your property, whole life insurance offers a lasting safety net for your loved ones, ensuring their financial stability even after you’re gone.
- Building Insurance: This policy covers the physical structure of the building, including its walls, roof, and foundation. It provides financial assistance for repairs or rebuilding in case of fire damage.
- Contents Insurance: This policy covers the belongings inside the building, such as furniture, appliances, electronics, and personal possessions. It offers financial support to replace or repair these items if they are damaged or destroyed by fire.
- Combined Building and Contents Insurance: This policy combines the coverage of building insurance and contents insurance, providing comprehensive protection for both the structure and its contents. It offers convenience and cost savings by consolidating multiple policies into one.
Perils Covered by Fire Insurance
Fire insurance policies typically cover a range of perils related to fire incidents.
- Fire: This is the primary peril covered, including damage caused by flames, smoke, and heat. The policy will cover repairs or replacement costs for the damaged property.
- Lightning: Damage caused by lightning strikes, such as electrical fires or structural damage, is often covered under fire insurance.
- Explosion: Explosions, whether caused by gas leaks, faulty appliances, or other factors, are typically covered by fire insurance policies.
- Smoke Damage: Smoke damage from a fire can be extensive and costly. Fire insurance policies usually cover the cost of cleaning and repairs related to smoke damage.
- Water Damage: Water damage caused by firefighting efforts, such as flooding from hoses, is typically covered by fire insurance policies.
Coverage Limitations
While fire insurance provides valuable protection, it has certain limitations.
- Exclusions: Fire insurance policies typically exclude certain perils, such as earthquakes, floods, and acts of war. It’s essential to review the policy carefully to understand the specific exclusions.
- Deductible: Most fire insurance policies have a deductible, which is the amount you are responsible for paying out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. The deductible can vary depending on the policy and coverage level.
- Policy Limits: Fire insurance policies have limits on the maximum amount of coverage they provide. It’s crucial to ensure the policy limits are sufficient to cover the full value of your property and belongings.
- Valuation: The value of your property and belongings is assessed to determine the amount of coverage you need. It’s essential to have your property and belongings properly valued to ensure adequate coverage.
Key Components of a Fire Insurance Policy

Fire insurance is a crucial component of financial protection for individuals and businesses. It provides coverage against losses arising from fire incidents, offering peace of mind and financial stability in the face of unforeseen circumstances. A standard fire insurance policy typically comprises several key components that define the terms of the agreement between the insured and the insurer.
These components are crucial for understanding the scope of coverage, obligations, and limitations associated with the policy.
Policy Declarations
The policy declarations section contains vital information about the insured and the insurance policy itself. It includes the insured’s name and address, the policy number, the effective date of coverage, the amount of insurance coverage, and the premium amount. The policy declarations serve as a foundational document that identifies the parties involved, the policy’s scope, and the financial aspects of the agreement.
Insuring Agreement
The insuring agreement Artikels the insurer’s promise to provide coverage for specific perils, such as fire, lightning, and other related events. It defines the scope of protection offered by the policy and the circumstances under which the insurer is obligated to compensate the insured for covered losses.
This section is a cornerstone of the policy, clearly defining the insurer’s commitment to indemnify the insured against covered perils.
Exclusions and Limitations
Every insurance policy contains exclusions and limitations that specify circumstances or events not covered by the policy. These provisions are essential for ensuring that the insurer’s risk is manageable and that the policy is not misused. Common exclusions in fire insurance policies include losses resulting from war, nuclear incidents, and intentional acts by the insured.
Limitations may include coverage limits, deductibles, and timeframes for filing claims.
Conditions
The conditions section Artikels the responsibilities and obligations of both the insured and the insurer. It covers aspects such as the insured’s duty to notify the insurer about a loss, cooperate with investigations, and maintain records. The conditions also address the insurer’s obligations, such as paying claims promptly and fairly, providing legal representation, and maintaining confidentiality.
Definitions, Fire insurance policy
The definitions section clarifies the meaning of specific terms used in the policy. It provides a glossary of technical terms and industry-specific language, ensuring clarity and consistency in interpreting the policy’s provisions.
Factors Influencing Fire Insurance Premiums
The cost of fire insurance premiums is determined by a multitude of factors, each contributing to the overall risk assessment of your property. These factors are carefully considered by insurance companies to calculate premiums that accurately reflect the potential financial burden of a fire-related incident.
Property Value
The value of your property is a primary factor in determining your fire insurance premium. The higher the value of your property, the greater the potential financial loss in case of a fire, leading to a higher premium. Insurance companies use various methods to assess property value, including market analysis, replacement cost estimates, and appraisal reports.
Location
The location of your property plays a significant role in premium calculations. Areas with higher fire risks, such as those with dense populations, dry climates, or proximity to hazardous industries, are generally associated with higher premiums. Factors like proximity to fire hydrants, fire station response times, and local building codes are also considered.
Construction Type
The type of construction used for your property has a direct impact on its fire resistance and the potential for damage. Properties constructed with fire-resistant materials, such as brick or concrete, generally have lower premiums compared to those built with wood or other flammable materials.
The presence of fire-suppression systems, like sprinklers, can also reduce premiums.
Occupancy
The intended use of your property influences the risk of fire and, consequently, your insurance premium. Commercial properties, with their higher levels of activity and potential for fire hazards, typically have higher premiums than residential properties. The specific type of business or industry operating in a commercial property also impacts premiums.
Risk Management Practices
Insurance companies reward property owners who implement proactive risk management practices to minimize the likelihood of fire. Factors such as the presence of smoke detectors, fire extinguishers, and regular maintenance programs can lead to lower premiums. In addition, comprehensive security measures, including alarms and surveillance systems, can further reduce premiums.
Claims History
Your past claims history is a key factor in premium calculations. Individuals or businesses with a history of filing claims, particularly for fire-related incidents, may face higher premiums. Insurance companies consider the frequency and severity of past claims to assess the likelihood of future claims.
Premium Calculation Methods
Insurance companies employ various methods to calculate premiums, each with its own nuances and considerations.
- Actuarial Methods:These methods rely on statistical data and historical claims information to estimate the likelihood of future losses. Actuarial models analyze various factors, including property value, location, construction type, and claims history, to develop a probability distribution of potential fire losses.
These probabilities are then used to calculate premiums that reflect the expected financial burden of future claims.
- Risk-Based Pricing:This approach focuses on identifying and assessing specific risks associated with each property. Insurance companies analyze factors such as occupancy, risk management practices, and the presence of fire-suppression systems to determine the level of risk associated with a property. Higher-risk properties typically have higher premiums, while lower-risk properties benefit from lower premiums.
- Competitive Pricing:Insurance companies also consider competitive factors when setting premiums. They analyze the pricing strategies of their competitors and adjust their premiums accordingly to remain competitive in the market. This approach ensures that premiums are in line with market trends and that insurance companies can attract and retain customers.
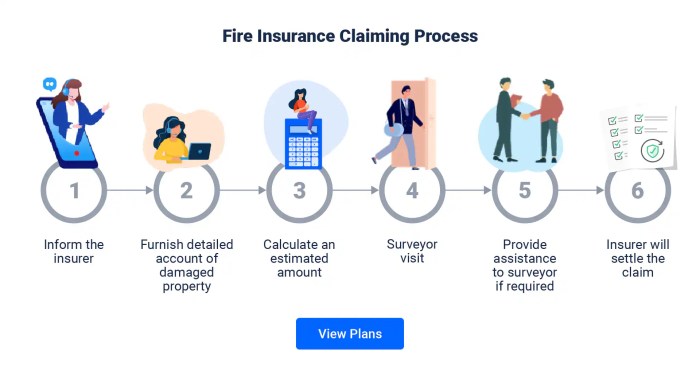
The Claims Process
The claims process is the mechanism through which you, as the policyholder, can receive compensation from your insurer for fire-related losses covered by your policy. This process involves several steps, each with its own set of requirements and procedures.
Steps Involved in Filing a Fire Insurance Claim
The process of filing a fire insurance claim typically involves these steps:
- Report the Fire:Immediately contact your insurer to report the fire. This notification is crucial for initiating the claims process and allows the insurer to start gathering necessary information.
- Secure the Property:Take immediate steps to secure the damaged property, preventing further damage and protecting any remaining belongings.
- Document the Loss:Gather evidence of the fire and its impact. This documentation will be essential for supporting your claim.
- File a Claim:Submit a formal claim to your insurer, providing all the necessary documentation.
- Claim Assessment:The insurer will assess your claim, verifying the extent of the damage and the coverage provided by your policy.
- Negotiation and Settlement:If your claim is approved, the insurer will negotiate a settlement amount based on the assessed damage and policy terms.
Documentation Required to Support a Claim
To support your fire insurance claim, you’ll need to provide comprehensive documentation to the insurer. This documentation typically includes:
- Proof of Loss:This document formally details the fire incident, including the date, time, location, and cause of the fire.
- Fire Department Report:Obtain a copy of the fire department’s report, which provides an official account of the incident.
- Photographs and Videos:Capture detailed photographs and videos of the damaged property, showcasing the extent of the fire damage.
- Inventory of Damaged Property:Create a detailed list of all damaged items, including their descriptions, purchase dates, and estimated values.
- Receipts and Documentation:Provide any available receipts, warranties, or other documentation related to the damaged property.
- Policy Documents:Ensure you have readily available copies of your fire insurance policy, including the coverage details and terms.
The Insurer’s Role in Assessing and Processing a Claim
Once you submit your claim, the insurer will undertake a thorough assessment process. This involves:
- Verification of the Incident:The insurer will verify the fire incident, ensuring it aligns with the information provided in your claim.
- Damage Assessment:The insurer will assess the extent of the damage caused by the fire, considering factors such as the structural damage, contents, and personal belongings.
- Policy Coverage Review:The insurer will review your fire insurance policy to determine the specific coverage provisions applicable to your claim.
- Claim Investigation:In certain cases, the insurer may conduct a more in-depth investigation to gather additional information and clarify the circumstances surrounding the fire.
- Negotiation and Settlement:Based on the assessment and policy terms, the insurer will negotiate a settlement amount with you.
Common Claim Scenarios and Potential Outcomes
The outcome of a fire insurance claim depends on various factors, including the extent of the damage, the cause of the fire, and the specific terms of your policy. Here are some common claim scenarios and their potential outcomes:
- Fire Damage to a Dwelling:If your dwelling is damaged by fire, your insurer may cover the cost of repairs or rebuilding, depending on the coverage limits and policy terms.
- Loss of Personal Property:Your insurer may cover the replacement cost of lost or damaged personal belongings, subject to coverage limits and deductibles.
- Business Interruption:If a fire disrupts your business operations, your policy may cover lost income and additional expenses incurred during the recovery period.
- Arson or Intentional Acts:If the fire is determined to be caused by arson or intentional acts, your insurer may investigate the incident and determine if coverage applies.
- Negligence or Lack of Maintenance:If the fire is caused by negligence or lack of proper maintenance, your insurer may deny coverage or reduce the settlement amount.
Benefits of Fire Insurance
Fire insurance provides a safety net that can protect you from the devastating financial consequences of a fire. It offers financial protection, peace of mind, and the ability to rebuild your life after a fire.
Financial Protection
Fire insurance can help you recover financially from the damage caused by a fire. It can cover a wide range of expenses, including:
- Repair or replacement of damaged property: This includes the structure of your home or building, as well as any personal belongings inside.
- Living expenses: If your home is uninhabitable, fire insurance can help cover the cost of temporary housing, food, and other essential expenses.
- Loss of income: If you are unable to work due to a fire, fire insurance may provide income replacement benefits.
- Liability claims: If someone is injured on your property due to a fire, fire insurance can help cover legal costs and settlements.
Peace of Mind and Security
Knowing that you have fire insurance can provide peace of mind and security. It can give you the confidence to focus on other important aspects of your life, knowing that you are protected in the event of a fire.
Avoiding Potential Financial Losses
Without fire insurance, you could face significant financial losses if your property is damaged or destroyed by fire. This could include:
- The cost of rebuilding or repairing your home or building: This can be extremely expensive, especially if you live in a high-cost area.
- The cost of replacing your personal belongings: This can include everything from furniture and appliances to clothing and electronics.
- Loss of income: If you are unable to work due to a fire, you could lose a significant amount of income.
- Legal costs: If you are sued for damages caused by a fire, you could face substantial legal costs.
Real-Life Scenarios
Fire insurance has helped countless individuals and families recover from devastating fires. Here are some examples:
- A family’s home was destroyed by a fire caused by a faulty electrical outlet. Their fire insurance policy covered the cost of rebuilding their home and replacing their belongings, allowing them to start over.
- A small business owner’s shop was damaged by a fire caused by a faulty heater. Their fire insurance policy covered the cost of repairs and lost income, enabling them to get their business back on track.
Summary
Fire insurance is more than just a piece of paper; it’s a promise, a commitment to safeguard your financial future in the face of unforeseen circumstances. By understanding the intricacies of fire insurance, you empower yourself to make informed decisions and protect your assets from the flames of disaster.
So, don’t wait until the flames are licking at your doorstep – take control of your future and secure the peace of mind that comes with knowing you’re protected.
Popular Questions
What happens if I have a fire and I don’t have fire insurance?
Without fire insurance, you’ll be responsible for covering the entire cost of repairs or rebuilding yourself. This could lead to significant financial hardship and even bankruptcy.
How much does fire insurance cost?
The cost of fire insurance varies depending on factors like the value of your property, its location, and the level of coverage you choose. It’s best to get quotes from multiple insurers to compare prices and find the best deal.
What if I have a fire caused by something not covered by my policy?
Fire insurance policies typically have exclusions, meaning certain events aren’t covered. It’s important to carefully read your policy to understand its limitations and consider additional coverage if needed.
What is a deductible and how does it work?
A deductible is the amount you’re responsible for paying out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible can lower your premium, but it also means you’ll have to pay more in case of a claim.