What are the benefits of universal life insurance? This question sets the stage for a journey into the realm of financial planning, offering a unique blend of life insurance protection and investment potential. Universal life insurance, often considered a flexible and customizable option, stands apart from traditional life insurance policies.
It allows you to control your coverage, tailor it to your evolving needs, and even build a cash value component that can potentially grow tax-deferred.
Imagine a financial tool that not only provides a safety net for your loved ones but also empowers you to build wealth and secure your future. This is the promise of universal life insurance, and in this exploration, we’ll uncover its strengths, flexibility, and potential for long-term financial success.
Understanding Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefit options. It’s a versatile policy that allows you to customize your coverage to fit your evolving needs and financial goals.
Flexible Premium Structure and Death Benefit Options
Universal life insurance provides a flexible premium structure, allowing you to adjust your payments based on your financial situation. You can choose to pay more than the minimum premium to build cash value faster, or you can pay less if you’re facing financial constraints.
The death benefit in a universal life insurance policy can also be adjusted. You can increase or decrease the amount of coverage based on your family’s needs and financial circumstances. This flexibility ensures that your insurance policy remains relevant as your life changes.
Cash Value Accumulation
A key feature of universal life insurance is the cash value component. A portion of your premium payments is allocated to a cash value account that earns interest. This cash value can be accessed through withdrawals, loans, or used to pay premiums.
The interest rate on the cash value account is typically variable, meaning it can fluctuate based on market conditions. However, the cash value component offers the potential for tax-deferred growth. This means that you won’t have to pay taxes on the interest earned until you withdraw the funds.
Benefits of Universal Life Insurance: What Are The Benefits Of Universal Life Insurance?
Universal life insurance offers a unique blend of coverage and investment features, making it a versatile option for individuals seeking long-term financial security. It provides flexibility in managing your policy, allowing you to adjust your coverage and premium payments to align with your changing needs and financial circumstances.
Flexibility and Control over Coverage
Universal life insurance empowers you to tailor your policy to your specific requirements. Unlike traditional life insurance policies, where coverage remains fixed, universal life insurance allows you to adjust your death benefit and premium payments over time. This flexibility can be beneficial in various scenarios:
- Increasing Coverage:If your family’s financial needs grow, you can increase your death benefit to provide greater financial protection. This can be particularly useful as your income rises, you have children, or you take on significant debt.
- Decreasing Coverage:As your children grow older and become financially independent, or as your debt decreases, you may decide to reduce your death benefit. This can lower your premium payments and potentially free up cash flow.
- Adjusting Premium Payments:Universal life insurance allows you to adjust your premium payments to fit your budget. If you experience financial hardship, you can temporarily reduce your payments, although this may impact your policy’s cash value growth. Conversely, if your financial situation improves, you can increase your payments to accelerate cash value accumulation.
Tax-Deferred Growth of Cash Value
Universal life insurance policies accumulate cash value, which grows tax-deferred. This means that you don’t have to pay taxes on the interest earned on your cash value until you withdraw it. This feature can be advantageous for long-term financial planning.
Here’s how tax-deferred growth works:
Your premium payments are split into two components: a death benefit premium and a cash value premium. The cash value premium is invested in a variety of sub-accounts, similar to a mutual fund. These sub-accounts offer different investment options, allowing you to choose an investment strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. The earnings on these investments are tax-deferred, meaning you don’t have to pay taxes on them until you withdraw the cash value.
This tax-deferred growth can significantly enhance your long-term savings.
Long-Term Financial Planning
Universal life insurance can be a valuable tool for long-term financial planning. Its flexibility and potential for tax-deferred growth make it suitable for various financial goals, including:
- Retirement Savings:You can use the cash value component of your universal life insurance policy as a supplementary retirement savings vehicle. You can withdraw the cash value tax-free for qualified expenses, such as medical costs or long-term care, after age 59 1/2.
- College Savings:The cash value can be used to fund your children’s education. You can withdraw it for educational expenses without incurring a tax penalty.
- Estate Planning:Universal life insurance can be a valuable tool for estate planning. The death benefit can help offset estate taxes and ensure that your loved ones are financially secure after your passing. You can also use the cash value to cover funeral expenses or other final expenses.
Customization and Flexibility
Universal life insurance offers a high degree of customization and flexibility, allowing policyholders to tailor their coverage to meet their changing needs and financial goals. This adaptability sets it apart from other types of life insurance, making it a potentially attractive option for individuals seeking a personalized approach to life insurance.
Adjusting Premiums and Death Benefit
The ability to adjust premiums and death benefit is a key feature of universal life insurance. Unlike traditional whole life insurance, where premiums and death benefit are fixed, universal life insurance allows policyholders to make changes based on their circumstances.
Policyholders can increase their premiums if they want to accumulate more cash value or increase their death benefit. Conversely, they can decrease their premiums if they need to reduce their monthly expenses or if their financial situation changes. This flexibility allows policyholders to adapt their coverage to their evolving needs, ensuring it remains relevant and valuable over time.
Borrowing Against Cash Value
Universal life insurance policies accumulate cash value, which is a portion of the premium that is invested and grows over time. Policyholders can borrow against this cash value, which can be used for various purposes such as paying for education, home renovations, or medical expenses.
Borrowing against cash value can be a useful tool for managing finances, but it’s essential to understand the implications. The interest rate charged on these loans is usually lower than other forms of borrowing, but the loan must be repaid, and interest accrues over time.
Failure to repay the loan can lead to a reduction in the death benefit or even the policy’s lapse.
Comparison to Other Permanent Life Insurance
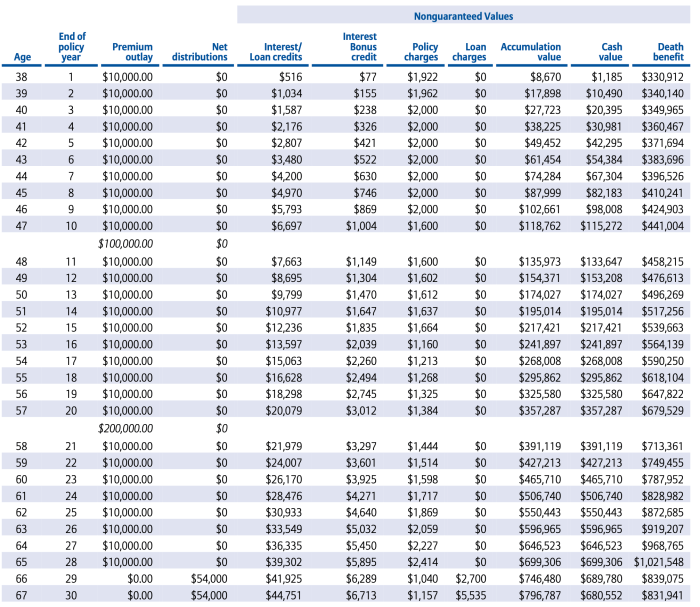
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance, which means it provides lifelong coverage and accumulates cash value. Other types of permanent life insurance include whole life insurance and indexed universal life insurance.
Universal life insurance offers flexibility and potential for growth, but it can be complex. Before you dive into the details, it’s crucial to understand how to compare life insurance policies, especially when considering different types. This comparison process will help you determine if universal life insurance aligns with your needs and financial goals.
Remember, the benefits of universal life insurance are most apparent when you understand its intricacies and compare it to other options.
- Whole Life Insurance:Offers a fixed premium and death benefit, making it less flexible than universal life insurance. It generally has a higher premium but provides guaranteed coverage and cash value growth.
- Indexed Universal Life Insurance:Similar to universal life insurance but links the cash value growth to a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. This can provide potential for higher returns but also carries more investment risk.
Considerations and Risks
While universal life insurance offers flexibility and potential for growth, it’s crucial to acknowledge its potential downsides and understand the factors that can impact your policy’s performance.Universal life insurance is a complex product, and its features can make it seem attractive, but it’s essential to weigh its advantages against its risks.
Higher Premiums
Universal life insurance premiums tend to be higher than traditional term life insurance policies. This is because universal life policies combine death benefit coverage with a cash value component, which requires additional premium payments. The cash value component allows policyholders to accumulate savings, but it also contributes to the higher premiums.
Potential for Cash Value Loss, What are the benefits of universal life insurance?
The cash value component of universal life insurance is invested in sub-accounts, which are subject to market fluctuations. If the investments perform poorly, the cash value may decline, potentially leading to a decrease in the death benefit or even policy lapse.
The potential for cash value loss is a significant risk associated with universal life insurance.
Understanding Policy Terms and Conditions
Universal life insurance policies can be complex and require careful review of the terms and conditions. Understanding the policy’s features, including the death benefit, premium payment schedule, cash value growth, and fees, is crucial. It’s essential to discuss any questions or concerns with a qualified insurance agent or financial advisor.
Investment Risk
The cash value component of universal life insurance is invested in sub-accounts, which can range from conservative to aggressive investments. The investment risk associated with these sub-accounts can impact the cash value growth. If the investments perform poorly, the cash value may not grow as expected, potentially leading to a lower death benefit or policy lapse.
It’s important to understand the level of risk associated with the sub-accounts and to choose investment options that align with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Real-World Examples and Applications

Universal life insurance is a versatile financial tool that can be tailored to meet a variety of needs. Its flexibility allows policyholders to adapt their coverage and investment strategies over time, making it a valuable option for various life stages and financial goals.
Illustrative Case Studies
Let’s explore real-world examples of how universal life insurance can be used effectively:
- Case 1: Estate Planning Imagine a successful entrepreneur, Sarah, who wants to ensure her family is financially secure after her passing. She uses universal life insurance to create a substantial death benefit that will cover estate taxes, funeral expenses, and provide financial support for her children’s education.
The policy’s cash value component also allows her to accumulate wealth over time, which she can access for future needs.
- Case 2: Retirement Savings John, a middle-aged professional, is looking for a way to supplement his retirement income. He chooses universal life insurance because it offers the potential for tax-deferred growth on his premiums. He allocates a portion of his premiums to the policy’s investment account, allowing his savings to grow over time.
When he retires, he can withdraw funds from the cash value component, providing an additional source of income.
- Case 3: Long-Term Care Planning Mary, a senior citizen, is concerned about the potential costs of long-term care. She opts for a universal life insurance policy with a long-term care rider. This rider allows her to access a portion of the policy’s death benefit to pay for long-term care expenses if she needs it.
This helps her protect her assets and ensure she receives the care she needs without depleting her savings.
Uses of Universal Life Insurance
Here’s a table summarizing different uses of universal life insurance:| Use Case | Benefit | Example | Considerations ||—|—|—|—|| Estate Planning | Provides a substantial death benefit to cover estate taxes, funeral expenses, and provide financial support for beneficiaries. | A wealthy individual uses universal life insurance to create a large death benefit to cover estate taxes and ensure their family’s financial security.
| Ensure the policy’s death benefit is sufficient to meet the individual’s estate planning goals. || Retirement Savings | Offers the potential for tax-deferred growth on premiums, allowing policyholders to accumulate wealth over time. | A middle-aged professional uses universal life insurance to supplement their retirement income, investing a portion of their premiums in the policy’s investment account.
| Monitor investment performance and adjust the policy’s investment strategy as needed. || Long-Term Care Planning | Provides access to a portion of the policy’s death benefit to cover long-term care expenses. | A senior citizen uses universal life insurance with a long-term care rider to protect their assets and ensure they receive the care they need.
| Ensure the policy’s death benefit is sufficient to cover potential long-term care costs. || College Savings | Allows policyholders to accumulate tax-deferred savings for their children’s education. | Parents use universal life insurance to save for their children’s college expenses, benefiting from tax-deferred growth on their premiums.
| Monitor the policy’s investment performance and adjust the policy’s investment strategy as needed. || Business Succession Planning | Provides a way for business owners to fund their business buy-sell agreements, ensuring a smooth transition of ownership. | A business owner uses universal life insurance to provide funds to buy out a deceased partner’s shares, ensuring the business remains stable.
| Ensure the policy’s death benefit is sufficient to cover the buy-out amount and the policy’s investment strategy is aligned with the business’s needs. |
Comparison to Other Life Insurance Options
Understanding how universal life insurance compares to other types of life insurance can help you make an informed decision about the best option for your needs. This section will provide a detailed comparison of universal life insurance with term life insurance, whole life insurance, and other permanent life insurance options.
Comparison of Life Insurance Types
To understand the differences between universal life insurance and other options, let’s look at a table comparing their key features, benefits, and drawbacks:
| Type of Insurance | Key Features | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Term Life Insurance |
|
|
|
| Whole Life Insurance |
|
|
|
| Universal Life Insurance |
|
|
|
| Indexed Universal Life Insurance |
|
|
|
| Variable Universal Life Insurance |
|
|
|
Choosing the Right Type of Life Insurance
The best type of life insurance for you depends on your individual needs and circumstances. Consider these factors:
- Your budget:Term life insurance is generally the most affordable option, while permanent life insurance can be more expensive.
- Your coverage needs:If you need coverage for a specific period (e.g., until your children are grown), term life insurance may be sufficient. If you need lifetime coverage, permanent life insurance is a better choice.
- Your risk tolerance:Universal life insurance and its variations offer more flexibility but also carry more risk. If you are comfortable with some risk, these options may be suitable. If you prefer a more predictable and secure approach, whole life insurance might be a better fit.
- Your financial goals:If you want to build cash value and have the potential for tax-deferred growth, permanent life insurance options may be worth considering.
Conclusion
Universal life insurance offers a compelling alternative for individuals seeking a life insurance policy that goes beyond basic protection. With its customizable features, potential for cash value growth, and ability to adapt to changing life circumstances, it can serve as a valuable tool for financial planning and wealth building.
While it’s important to understand the potential risks and carefully consider your individual needs, universal life insurance can provide a solid foundation for achieving your long-term financial goals.
Key Questions Answered
What are the main differences between universal life insurance and whole life insurance?
While both are permanent life insurance options, universal life insurance offers more flexibility in terms of premiums, death benefit, and cash value growth. Whole life insurance typically has fixed premiums and a guaranteed death benefit, while universal life insurance allows for adjustments based on your needs and market conditions.
Can I withdraw from the cash value in a universal life insurance policy?
Yes, you can typically withdraw from the cash value, but withdrawals may be subject to taxes and may reduce the death benefit. It’s crucial to understand the terms and conditions of your policy regarding withdrawals.
How does the investment risk associated with universal life insurance work?
The cash value component of universal life insurance is often invested in sub-accounts, which can fluctuate in value based on market performance. This means there’s a potential for both growth and loss. The investment strategy chosen for your cash value will impact its growth potential.