How much does health insurance cost? It’s a question on everyone’s mind, especially as healthcare costs continue to climb. But understanding the factors that influence premiums and the different types of plans available can help you make informed decisions about your health coverage.
From deductibles to copayments, there’s a lot to consider, and knowing the ins and outs can save you money and stress in the long run.
This guide will break down the key factors that determine health insurance costs, explore the various plan options, and provide tips on how to navigate the process of selecting the best coverage for your individual needs. We’ll also discuss strategies for reducing your premiums and maximizing your benefits, so you can feel confident in your health insurance choices.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Your health insurance premium is the monthly amount you pay to maintain your coverage. Several factors determine how much you pay, and understanding them can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance plan.
Age
Your age is a significant factor in determining your health insurance premium. Generally, younger people tend to be healthier and require less medical care, leading to lower premiums. As you age, the likelihood of health issues increases, which can lead to higher premiums.
For example, a 25-year-old individual might pay significantly less for health insurance than a 65-year-old individual.
Location
The cost of living and healthcare expenses vary significantly across different locations. Health insurance premiums are often higher in areas with a higher cost of living and higher healthcare utilization rates. For instance, health insurance premiums in major metropolitan areas tend to be higher than in rural areas.
Health Status
Your health status is a major factor in determining your health insurance premium. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of significant medical expenses may face higher premiums. Insurance companies assess your health risk based on factors like medical history, current health conditions, and family history.
Figuring out health insurance costs can be a real head-scratcher, especially when you’re comparing plans and premiums. But, if you’re thinking about long-term financial security, you might also want to consider life insurance. Have you ever wondered what are the rates for whole life insurance?
? It’s a different beast altogether, but it can provide peace of mind for your loved ones in the long run. And, of course, it’s just as important to shop around for the best health insurance plan that fits your budget and needs.
Lifestyle Choices
Your lifestyle choices can also impact your health insurance premium. For instance, individuals who engage in unhealthy habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption may face higher premiums. Insurance companies consider these factors because they increase the likelihood of future health issues and higher healthcare costs.
Individual vs. Family Health Insurance Plans, How much does health insurance cost?
Individual health insurance plans cover a single person, while family health insurance plans cover multiple individuals, typically spouses and children. Family plans typically cost more than individual plans because they cover a larger group of people, increasing the potential for healthcare expenses.
The exact cost difference can vary depending on the specific plan and the number of individuals covered.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
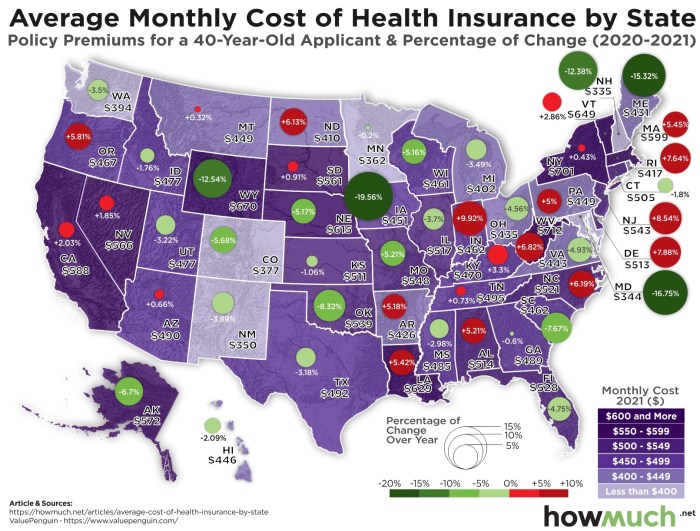
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like trying to decipher a foreign language. But fear not, because understanding the different types of health insurance plans is easier than you think. There are several types of plans available, each with its own set of rules and costs.
Let’s dive into the most common types.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
HMOs are known for their emphasis on preventive care and cost-effectiveness. They usually have a network of doctors and hospitals you must use for coverage.
HMOs often require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as your gatekeeper to specialists.
- You generally need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist.
- HMOs typically have lower premiums than other plans.
- They often have lower copayments and deductibles.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see doctors and hospitals both in and out of their network.
You’ll pay less if you stay within the network, but you still have the option to go outside the network for a higher price.
- PPOs usually have higher premiums than HMOs.
- They generally have higher deductibles and copayments.
- You don’t need a referral to see a specialist.
Point-of-Service (POS)
POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, giving you the option to choose between in-network and out-of-network care.
You typically need a referral from your PCP for in-network care, but you can go out of network without a referral.
- POS plans often have premiums somewhere between HMOs and PPOs.
- They generally have deductibles and copayments that fall somewhere between HMOs and PPOs.
- They offer more flexibility than HMOs but less than PPOs.
Comparing Plan Types
Here’s a table summarizing the key features of each plan type:
| Feature | HMO | PPO | POS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network | Limited to network providers | In-network and out-of-network providers | In-network and out-of-network providers |
| Referral Required | Yes, for specialists | No | Yes, for in-network care |
| Premiums | Lower | Higher | Medium |
| Deductibles | Lower | Higher | Medium |
| Copayments | Lower | Higher | Medium |
| Flexibility | Less | More | Moderate |
Understanding Your Health Insurance Costs
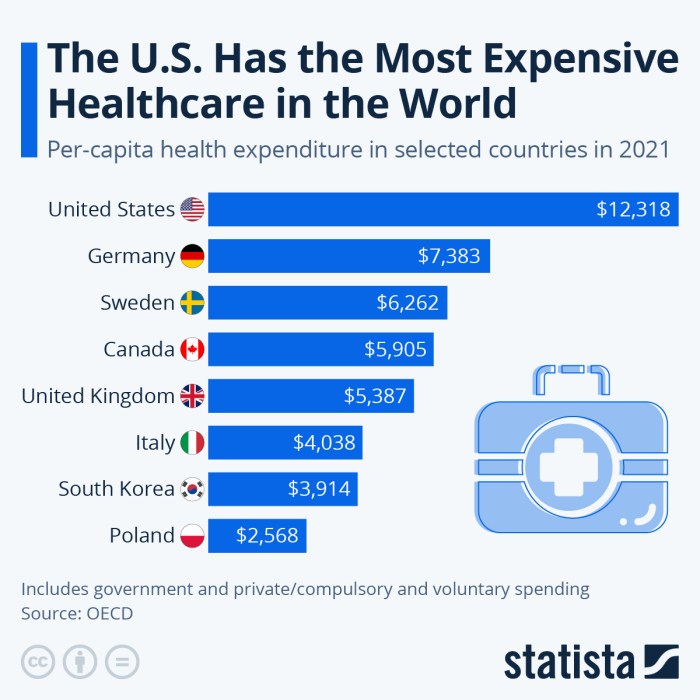
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a secret code. But don’t worry, understanding your costs doesn’t have to be a headache. Let’s break down the key components that make up your health insurance bill.
Components of a Health Insurance Premium
Your health insurance premium is the monthly fee you pay to keep your insurance policy active. Think of it as your membership dues to the healthcare club. The premium is calculated based on several factors, including your age, location, chosen plan, and whether you smoke.
Here’s a closer look at the elements that make up your premium:
- Base Premium:This is the core cost of your insurance policy, determined by factors like your age, location, and chosen plan. For example, a 30-year-old living in a city might have a higher base premium than a 20-year-old living in a rural area.
- Additional Charges:These are extra fees that can be added to your base premium, depending on your individual circumstances. Examples include:
- Tobacco Surcharge:If you smoke, you’ll likely face a higher premium. This is because smokers tend to have higher healthcare costs due to increased risk of smoking-related illnesses.
- Family Coverage:Adding family members to your policy will increase your premium. The more people covered, the higher the cost.
- Deductible:This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in. A higher deductible usually means a lower premium. For example, a deductible of $2,000 means you’ll pay the first $2,000 of your healthcare costs yourself before your insurance starts covering the rest.
- Co-insurance:This is the percentage of your healthcare costs that you share with your insurance company after your deductible is met. For example, a 20% co-insurance means you pay 20% of the cost of your healthcare services after your deductible is met.
- Co-payments:These are fixed fees you pay for specific services, such as doctor’s visits or prescription drugs. For example, you might pay a co-payment of $20 for a doctor’s visit or $10 for a generic prescription.
Premium vs. Out-of-Pocket Expense
It’s important to distinguish between your premium and out-of-pocket expenses. Your premium is the monthly fee you pay to maintain your insurance policy, while out-of-pocket expenses are the costs you pay directly for healthcare services.
“Think of your premium as your monthly rent for your healthcare coverage, while your out-of-pocket expenses are like the utilities you pay for using that coverage.”
For example, your premium might be $300 per month, while your out-of-pocket expenses could include your deductible, co-insurance, and co-payments. These out-of-pocket expenses can vary depending on your plan and the healthcare services you receive.
Estimating Your Annual Health Insurance Costs
To get a rough estimate of your annual health insurance costs, you can use the following formula:
“Annual Health Insurance Costs = (Monthly Premium x 12) + Estimated Out-of-Pocket Expenses”
Let’s say your monthly premium is $300 and you estimate your annual out-of-pocket expenses to be $1,
000. Your annual health insurance costs would be
“(300 x 12) + 1000 = 3600 + 1000 = $4600”
Keep in mind that this is just an estimate, and your actual costs may vary. It’s always a good idea to consult with your insurance provider or a financial advisor to get a more accurate picture of your expected health insurance costs.
Strategies for Reducing Health Insurance Costs: How Much Does Health Insurance Cost?
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like a maze, especially when it comes to finding ways to lower your premiums. But don’t fret! There are several strategies you can employ to make your health insurance more affordable.
Shopping Around for Plans
Just like you wouldn’t buy the first car you see, don’t settle for the first health insurance plan offered to you. The health insurance market is competitive, and different insurers offer varying plans with different premiums. Take the time to compare plans from multiple insurers to find the best deal for your needs.
Online comparison tools can be your best friend. Websites like eHealth, HealthCare.gov, and others allow you to enter your details and see a range of plans from various insurers, side-by-side. This makes it easier to spot the most cost-effective options.
Enrolling in a Health Savings Account (HSA)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are a great way to save money on health insurance premiums and healthcare expenses. HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts specifically for healthcare costs.
- Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income and potentially lowering your tax bill.
- Earnings on HSA funds grow tax-free, allowing your savings to accumulate more quickly.
- Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free, making it a more cost-effective way to pay for healthcare compared to using traditional savings.
However, it’s crucial to note that HSAs are only available to those enrolled in high-deductible health plans (HDHPs). This means you’ll have a higher deductible than traditional plans, but the potential savings from HSA contributions and tax benefits can offset this.
Making Healthy Lifestyle Choices
It may seem obvious, but leading a healthier lifestyle can actually impact your health insurance premiums. Insurers often offer discounts for individuals who demonstrate healthy habits.
- Quitting smoking: Many insurers offer discounts for non-smokers.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Individuals who maintain a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) might qualify for discounts.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Insurers might offer discounts for individuals who demonstrate regular physical activity, such as gym memberships or participation in fitness programs.
While these discounts might not be substantial, they can still contribute to lowering your overall healthcare costs.
Negotiating with Your Employer
If you’re getting your health insurance through your employer, you might have some leverage to negotiate lower premiums.
- Explore options for lower coverage levels: If you’re young and healthy, you might be able to opt for a plan with a higher deductible and lower premium.
- Consider enrolling in a plan with a larger network: While a smaller network might offer lower premiums, a larger network provides more choices for healthcare providers, potentially leading to lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Negotiate a contribution increase: You can offer to increase your contribution to your health insurance premiums in exchange for a lower premium from your employer.
It’s important to discuss your options with your employer and see what’s possible.
Seeking Assistance from Government Programs
For individuals struggling to afford health insurance, there are government programs available to provide assistance.
- Medicaid: Medicaid is a government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility requirements vary by state.
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA): The ACA provides subsidies to individuals and families who meet certain income requirements, helping them afford health insurance.
- CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program): CHIP provides health insurance coverage to children in families who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but can’t afford private health insurance.
You can learn more about these programs and eligibility requirements through the official websites of your state’s Medicaid program and the HealthCare.gov website.
Utilizing Resources and Organizations
Several organizations and resources can help you find affordable health insurance options.
- Your State’s Health Insurance Marketplace: Each state has its own health insurance marketplace, which allows you to compare plans and enroll in coverage.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC provides information and resources on health insurance, including tips for finding affordable coverage.
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS is the federal agency responsible for administering Medicare and Medicaid. They also offer resources and information on health insurance.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to these organizations for assistance in navigating the complexities of health insurance.
Navigating Health Insurance Costs
The process of selecting and enrolling in a health insurance plan can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. With a little planning and research, you can navigate the process effectively and find a plan that meets your needs and budget.
Comparing Quotes from Different Insurance Providers
Comparing quotes from different insurance providers is essential for finding the best value. Insurance companies offer various plans with different coverage, deductibles, and premiums. Here’s how to compare quotes effectively:
- Use a health insurance comparison website:Websites like HealthCare.gov, eHealth, and insurance providers’ websites allow you to compare plans side-by-side based on your location, age, and other factors.
- Consider your individual needs:Before comparing quotes, determine your healthcare needs. Factors to consider include your current health status, expected healthcare utilization, and desired coverage levels.
- Look beyond the monthly premium:While the monthly premium is important, it’s not the only factor to consider. Compare deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums as well.
Understanding the Fine Print of Insurance Policies
Once you’ve narrowed down your choices, carefully review the policy details. Understanding the fine print can help you avoid surprises and ensure you’re getting the coverage you need.
- Coverage details:Pay close attention to the types of services covered, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and preventive care. Some plans may have limitations or exclusions.
- Deductibles and copayments:Understand how much you’ll pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles often mean lower premiums, but you’ll have to pay more before your insurance covers expenses.
- Out-of-pocket maximums:This is the maximum amount you’ll pay for healthcare expenses in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance will cover the remaining costs.
- Network limitations:Check if your preferred doctors and hospitals are in the plan’s network. Out-of-network services may have higher costs or require pre-authorization.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when selecting health insurance:
- Not comparing quotes:Don’t settle for the first plan you find. Compare quotes from multiple insurance providers to ensure you’re getting the best value.
- Choosing a plan based solely on price:While price is important, don’t sacrifice coverage for a lower premium. Consider your healthcare needs and expected utilization.
- Ignoring the fine print:Take the time to read through the policy details carefully. Understanding the coverage, deductibles, and other terms can help you avoid surprises later.
Closing Summary

Navigating health insurance costs can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can find affordable and comprehensive coverage that meets your specific needs. By understanding the factors that influence premiums, exploring different plan options, and utilizing cost-saving strategies, you can make informed decisions that protect your health and your wallet.
Remember, your health is your most valuable asset, and having the right insurance can give you peace of mind and financial security.
FAQ Explained
What is the average cost of health insurance?
The average cost of health insurance varies significantly depending on factors like age, location, health status, and the type of plan you choose. It’s best to get personalized quotes from different insurance providers to determine your specific costs.
How can I find affordable health insurance?
There are several strategies for finding affordable health insurance, including shopping around for plans, enrolling in a health savings account (HSA), and making healthy lifestyle choices to reduce your risk of health problems.
What are the most common types of health insurance plans?
The most common types of health insurance plans include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Point-of-Service (POS) plans. Each plan type offers different coverage options, deductibles, and copayments.